简介
-
Spring 从 3.1 开始定义了 org.springframework.cache.Cache 和 org.springframework.cache.CacheManager 接口来统一不同的缓存技术; 并支持使用 JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
-
Cache 接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合; Cache 接 口 下 Spring 提 供 了 各 种 xxxCache 的 实 现 ; 如 RedisCache , EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache 等:
-
每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring 会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已 经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓 存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
-
使用 Spring 缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
- 确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略;
- 从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据.
-
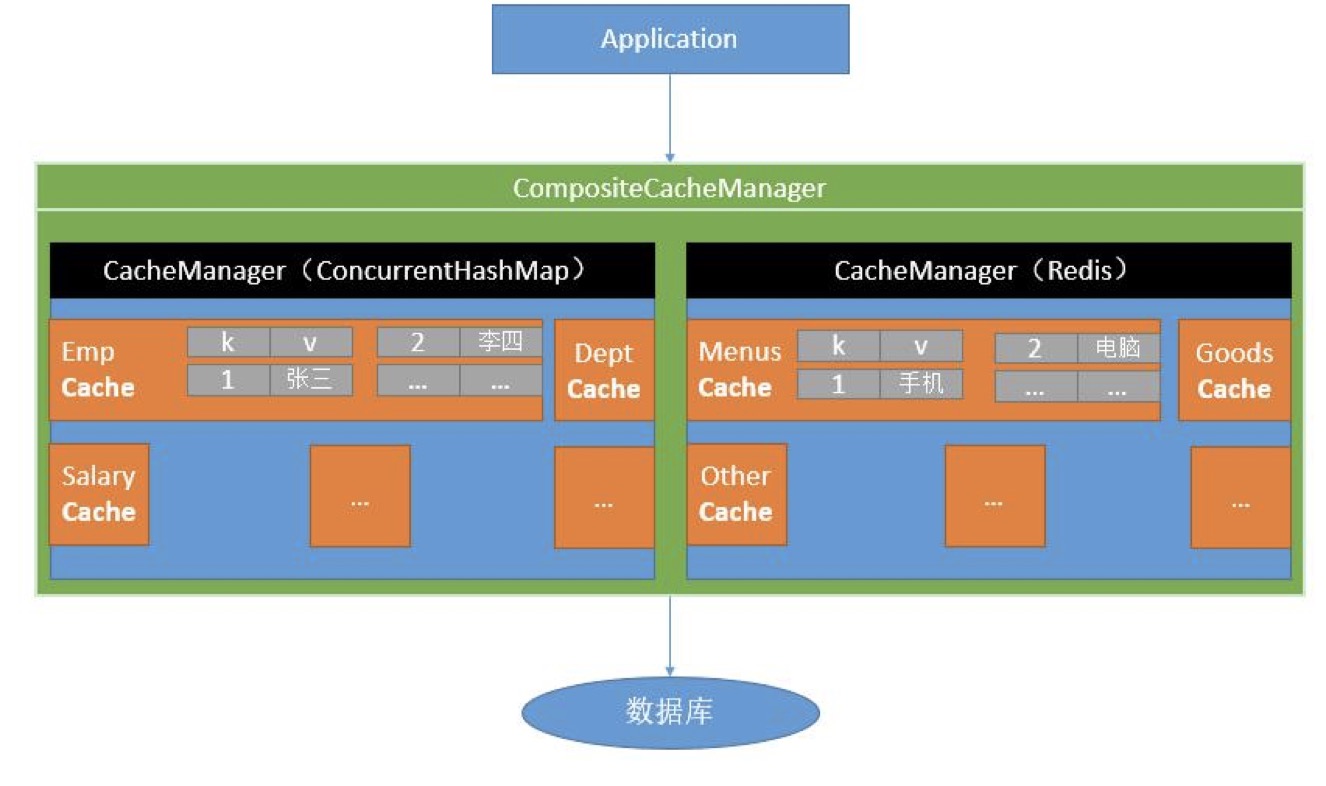
Spring Cache常用注解
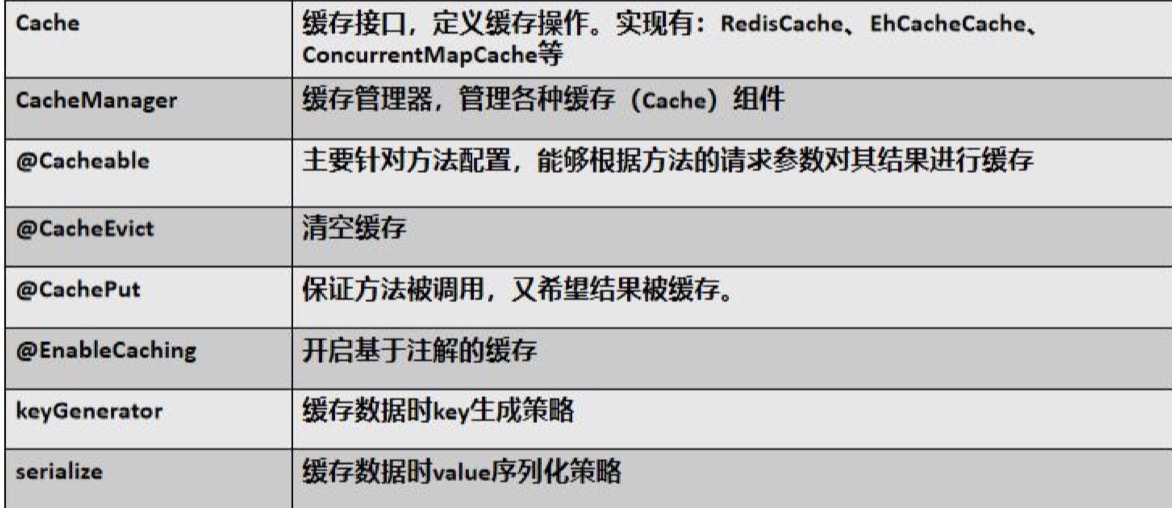
其中, 失效模式注解的参数:

使用
引依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
写配置
spring.cache.type=redis
spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=3600000
spring.cache.redis.use-key-prefix=true
spring.cache.redis.cache-null-values=true
加注解
- 应用入口
@EnableRedisHttpSession //开启springsession
@EnableCaching //开启缓存功能
@MapperScan("com.learn.demomarket.product.dao")
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemomarketProductApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemomarketProductApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 如果写自动配置类:
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class MyCacheConfig {
// @Autowired
// public CacheProperties cacheProperties;
/**
* 配置文件的配置没有用上
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties) {
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
// config = config.entryTtl();
config = config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()));
config = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();
//将配置文件中所有的配置都生效
if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {
config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());
}
if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {
config = config.prefixKeysWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());
}
if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {
config = config.disableCachingNullValues();
}
if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {
config = config.disableKeyPrefix();
}
return config;
}
}
- 使用
/**
* 每一个需要缓存的数据我们都来指定要放到那个名字的缓存。【缓存的分区(按照业务类型分)】
* 代表当前方法的结果需要缓存,如果缓存中有,方法都不用调用,如果缓存中没有,会调用方法。最后将方法的结果放入缓存
* 默认行为
* 如果缓存中有,方法不再调用
* key是默认生成的:缓存的名字::SimpleKey[](自动生成key值)
* 缓存的value值,默认使用jdk序列化机制,将序列化的数据存到redis中
* 默认时间是 -1:
*
* 自定义操作:key的生成
* 指定生成缓存的key:key属性指定,接收一个Spel
* 指定缓存的数据的存活时间:配置文档中修改存活时间
* 将数据保存为json格式
*
*
* 4、Spring-Cache的不足之处:
* 1)、读模式
* 缓存穿透:查询一个null数据。解决方案:缓存空数据
* 缓存击穿:大量并发进来同时查询一个正好过期的数据。解决方案:加锁 ? 默认是无加锁的;使用sync = true来解决击穿问题
* 缓存雪崩:大量的key同时过期。解决:加随机时间。加上过期时间
* 2)、写模式:(缓存与数据库一致)
* 1)、读写加锁。
* 2)、引入Canal,感知到MySQL的更新去更新Redis
* 3)、读多写多,直接去数据库查询就行
*
* 总结:
* 常规数据(读多写少,即时性,一致性要求不高的数据,完全可以使用Spring-Cache):写模式(只要缓存的数据有过期时间就足够了)
* 特殊数据:特殊设计
*
* 原理:
* CacheManager(RedisCacheManager)->Cache(RedisCache)->Cache负责缓存的读写
* @return
*/
@Cacheable(value = {"category"},key = "#root.method.name",sync = true)
@Override
public List<CategoryEntity> getLevel1Categorys() {
System.out.println("getLevel1Categorys........");
long l = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<CategoryEntity> categoryEntities = this.baseMapper.selectList(
new QueryWrapper<CategoryEntity>().eq("parent_cid", 0));
System.out.println("消耗时间:"+ (System.currentTimeMillis() - l));
return categoryEntities;
}
@Cacheable(value = "category",key = "#root.methodName")
@Override
public Map<String, List<Catelog2Vo>> getCatalogJson() {
System.out.println("查询了数据库");
//将数据库的多次查询变为一次
List<CategoryEntity> selectList = this.baseMapper.selectList(null);
//1、查出所有分类
//1、1)查出所有一级分类
List<CategoryEntity> level1Categorys = getParent_cid(selectList, 0L);
//封装数据
Map<String, List<Catelog2Vo>> parentCid = level1Categorys.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(k -> k.getCatId().toString(), v -> {
//1、每一个的一级分类,查到这个一级分类的二级分类
List<CategoryEntity> categoryEntities = getParent_cid(selectList, v.getCatId());
//2、封装上面的结果
List<Catelog2Vo> catelog2Vos = null;
if (categoryEntities != null) {
catelog2Vos = categoryEntities.stream().map(l2 -> {
Catelog2Vo catelog2Vo = new Catelog2Vo(v.getCatId().toString(), null, l2.getCatId().toString(), l2.getName().toString());
//1、找当前二级分类的三级分类封装成vo
List<CategoryEntity> level3Catelog = getParent_cid(selectList, l2.getCatId());
if (level3Catelog != null) {
List<Catelog2Vo.Category3Vo> category3Vos = level3Catelog.stream().map(l3 -> {
//2、封装成指定格式
Catelog2Vo.Category3Vo category3Vo = new Catelog2Vo.Category3Vo(l2.getCatId().toString(), l3.getCatId().toString(), l3.getName());
return category3Vo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
catelog2Vo.setCatalog3List(category3Vos);
}
return catelog2Vo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
return catelog2Vos;
}));
return parentCid;
}
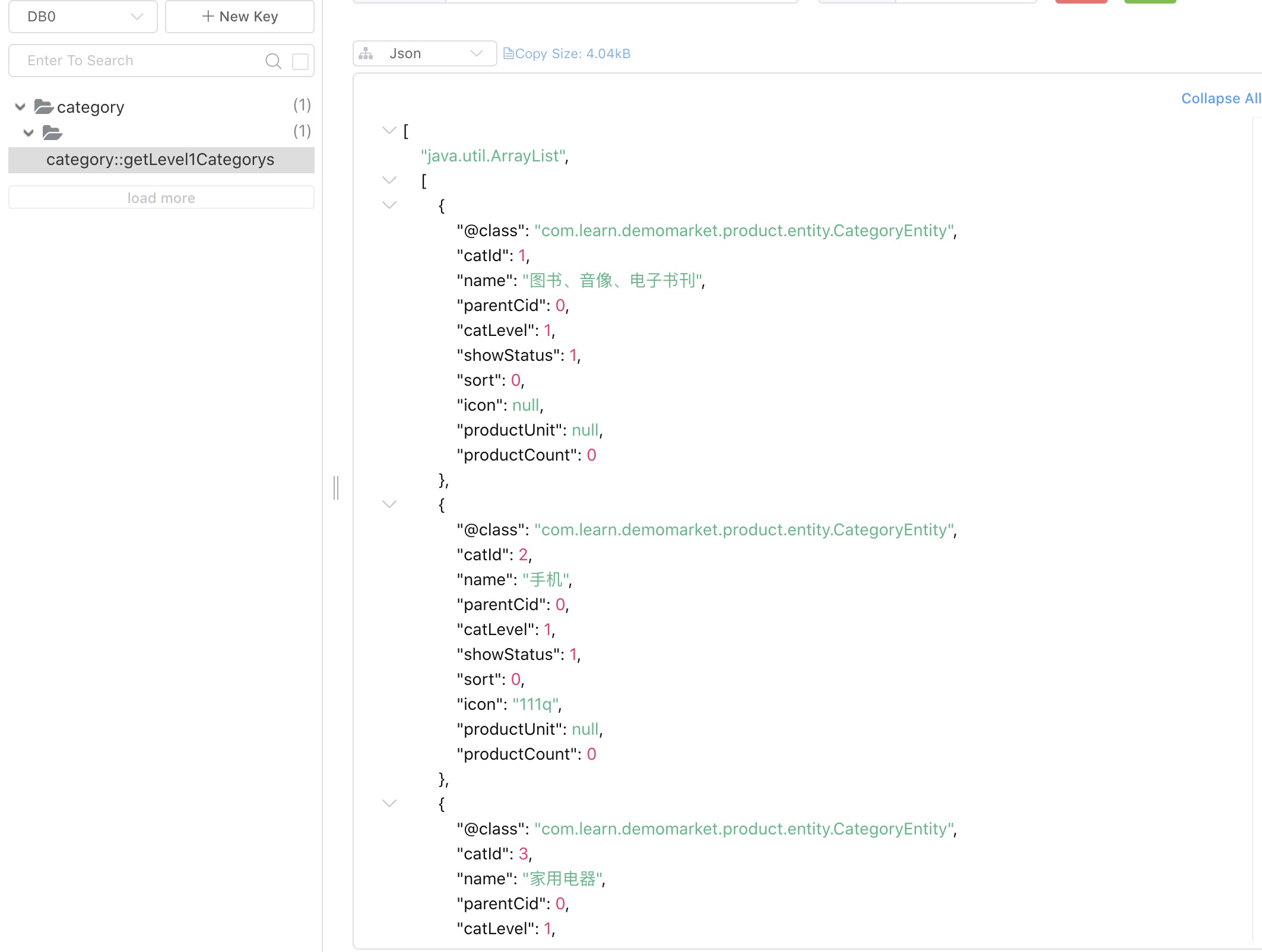
效果
经过配置, 能够以String类型给Redis里缓存住结果对象.
缓存失效模式@CacheEvict注解使用
/**
* 级联更新所有关联的数据
*
* @CacheEvict:失效模式
* @CachePut:双写模式,需要有返回值
* 1、同时进行多种缓存操作:@Caching
* 2、指定删除某个分区下的所有数据 @CacheEvict(value = "category",allEntries = true)
* 3、存储同一类型的数据,都可以指定为同一分区
* @param category
*/
// @Caching(evict = {
// @CacheEvict(value = "category",key = "'getLevel1Categorys'"),
// @CacheEvict(value = "category",key = "'getCatalogJson'")
// })
@CacheEvict(value = "category",allEntries = true) //删除某个分区下的所有数据
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
@Override
public void updateCascade(CategoryEntity category) {
RReadWriteLock readWriteLock = redissonClient.getReadWriteLock("catalogJson-lock");
//创建写锁
RLock rLock = readWriteLock.writeLock();
try {
rLock.lock();
this.baseMapper.updateById(category);
categoryBrandRelationService.updateCategory(category.getCatId(), category.getName());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
rLock.unlock();
}
//同时修改缓存中的数据
//删除缓存,等待下一次主动查询进行更新
}
Spring Cache常见一致性问题的解决思路
- 读模式
- 缓存穿透: 在缓存中存储null值, 防止空值再查数据库;
- 缓存击穿: 加锁(读写锁一般就够);
- 缓存雪崩: 一般小型系统没事的. 可以考虑加随机过期时间.
- 写模式
- 读写加锁:保证缓存与数据库一致.适用于读多写少的情况;
- 使用Canal中间件, 假装成MySQL从库感知主库变化然后修改缓存. 一般奥卡姆剃刀, 还是少加点中间件吧;
- 对于读多写也多的, 直接查数据库吧.
